IMAQ Read Barcode 2 VI
- Updated2023-02-21
- 12 minute(s) read
Requires: NI Vision Development Module
Reads common 1D barcode types, including Codabar, Code 39, Code 93, Code 128, EAN 8, EAN 13, Interleaved 2 of 5, MSI, UPCA, Pharmacode, and RSS Limited (GS1 DataBar Limited). For more information, see 2D Code Regeneration Concepts.
 |
Tip It is recommended that you disable the Pharmacode barcodes unless you are specifically decoding barcodes of this type. Pharmacodes are simple, and many barcodes can be mistaken for this type. |
 |
Tip When using multiple barcodes that include Code 39, Code 93, or Interleaved 2 of 5, it is recommended that you set the Validate parameter to FALSE (unchecked). |
Supported Image Types







 |
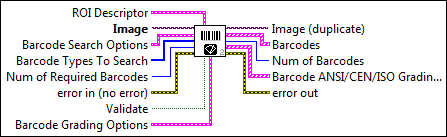
ROI Descriptor is a descriptor that defines the region of interest within which the code is located. The ROI must be a rectangle or rotated rectangle with a rotation of 0 degrees. If the ROI descriptor is empty or not connected, the entire image is considered to be the region.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
Image is a reference to the source image. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
Barcode Search Options is a cluster that contains the barcode search options to use when searching for barcodes in the image.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
Barcode Types To Search is an array of Barcode types to search in the image.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
Num of Required Barcodes defines the number of barcodes to be read from the image. The default is 1. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
error in (no error) describes the error status before this VI or function runs. The default is no error. If an error occurred before this VI or function runs, the VI or function passes the error in value to error out. This VI or function runs normally only if no error occurred before this VI or function runs. If an error occurs while this VI or function runs, it runs normally and sets its own error status in error out. Use the Simple Error Handler or General Error Handler VIs to display the description of the error code. Use error in and error out to check errors and to specify execution order by wiring error out from one node to error in of the next node.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
Validate specifies whether to validate the barcode's data. If the barcode type is Codabar, Code 39, or Interleaved 2 of 5, the error correction information is used to validate the results. For all other barcode types, either no validation is performed or the validation is performed automatically because the type requires it. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
Barcode Grading Options provides options for Barcode Grading
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
Image (duplicate) is the reference to the image that contains the barcode. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
Barcodes contains the information about the barcode that was read.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
Num of Barcodes outputs the number of barcodes that were read. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
Barcode ANSI/CEN/ISO Grading Report is a cluster detailing the grading information of the barcode. It has 9 grades and 1 overall grade. All the grades displayed are the average of the grades over ten scan lines across the barcode, as recommended by the ANSI/CEN/ISO Bar Code Print Quality standard.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
error out contains error information. If error in indicates that an error occurred before this VI or function ran, error out contains the same error information. Otherwise, it describes the error status that this VI or function produces. Right-click the error out indicator on the front panel and select Explain Error from the shortcut menu for more information about the error.
|
Examples
Refer to the following for examples that use this VI.
- LabVIEW\examples\Vision\Barcode\Read 1D Barcode.vi
- LabVIEW\examples\Vision\Image Management\Unwrap Barcode.vi










